计算几何小结
向量线段相关
点积:
$a.x * b.x+a.y*b.y$
叉积:
$a.xb.y-a.yb.x$
转角公式:
逆时针旋转角度$B$
原:$(cosAr,sinAr)$
现:$(cos(A+B)r,sin(A+B)r)=((cosAcosB-sinAsinB)r,(sinAcosB+cosAsinB)r)$
即:$(x,y)->(xcosB-ysinB,xsinB+ycosB)$
极角排序:
两种方法:
方法一:$atan2()$
这是一个给定三角形对边和邻边算角的函数,在$cmath$库中
对每个向量求$angle=atan2(a.y,a.x)$后直接排序即可
方法二:叉积
叉积的正负可以判断左右关系,所以在最大跨角不超过180度的时候可以非常好地实现,否则有可能随机一个起点绕好几圈(我比较倾向于这个)
两直线夹角:
若两个向量都是从原点出发,则可以很方便地用
$\theta=atan2(x \times y,x*y)$
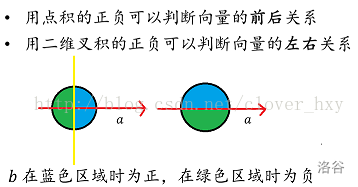
叉积是平行四边形,底乘高;点积是底乘投影。
更特殊点,该夹角是有向夹角,从$x$向量旋转到$y$,逆时针是正角、顺时针是负角。
两直线交点:
面积比->线段比->定比分点
node crosss(node a1,node a2,node b1,node b2){
node a=a2-a1,b=b2-b1,c=b1-a1;
if(fabs(b*a)<1e-12) return (node){-1e9,-1e9};
double t=(b*c)/(b*a);
return a1+(a^t);
}
|
判断两直线是否相交:
$a1,a2,b1,b2$为两条直线的两个端点
如果满足$(b1-a1)×(b1-a2)$和$(b2-a1)×(b2-a2)$不同号,并且$(a1-b1)×(a1-b2)$和$(a2-b1)×(a2-b2)$不同号,则两线段相交,叫跨立实验。
多边形相关:
凸包:
找到最下的点设为原点,将剩下的点用叉积极角排序
用单调栈维护凸包,当叉积为非负时需要弹栈
struct node{
double x,y;
inline bool operator < (node a)const{return x<a.x||(x==a.x&&y<a.y);}
}p[maxn],st[maxn];
inline double v_pro(node a,node b,node c){
return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(c.x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y);
}
int main(){
sort(p+1,p+1+n);
st[0]=p[1];
for(re int i=1;i<=n;i++){
while(top&&v_pro(st[top],st[top-1],p[i])>=0)--top;
st[++top]=p[i];
}
st[top=0]=p[n];
for(re int i=n-1;i;i--){
while(top&&v_pro(st[top],st[top-1],p[i])>=0)--top;
st[++top]=p[i];
}
}
|
判断点是否在多边形内:
从该点向右引射线,与多边形交奇数次即在其内。
顺时针$+1$,逆时针$-1$,注意与顶点重合的情况
$CF375C\ \ \ \ \ Circling Round Treasures$
判断点是否在凸包内:
先判定和边界的关系
然后找到与其极角相邻的两点,凭此判断
须保证$A[1]=(0,0)$
ll inside(node a){
if(a*A[1]>0||A[tot]*a>0) return 0;
ll pos=lower_bound(A+1,A+tot+1,a,cmp2)-A-1;
return (a-A[pos])*(A[pos%tot+1]-A[pos])<=0;
}
|
求多边形面积:
逆时针极角排序后直接用叉积求
double CalcS(){
double res=0;
for(int i=2;i<node;i++) res+=(A[i]-A[1])*(A[i+1]-A[1]);
return res/2;
}
|
三角形重心:
三点各坐标的平均值$(\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3},\frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3})$
算法:
旋转卡壳:
利用凸包上一些奇妙的单调性,求解
多边形直径
多边形宽度
最小面积矩形覆盖
等等
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define re register
const int maxn=5e4+5;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
struct node{
int x,y;
}p[maxn],p0,s[maxn];
int n,top;
ll ans=INF;
inline bool cmp(node a,node b){
double A=atan2(a.y-p0.y,a.x-p0.x);
double B=atan2(b.y-p0.y,b.x-p0.x);
if(A!=B)return A<B;
return a.x<b.x;
}
inline ll V_pro(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2){
return (1ll*x1*y2-1ll*x2*y1);
}
inline ll compare(node a,node b,node c){
return V_pro((b.x-a.x),(b.y-a.y),(c.x-a.x),(c.y-a.y));
}
inline void find(){
p0=(node){INF,INF};
int k=0;
for(re int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(p0.y>p[i].y||(p0.y==p[i].y&&p0.x>p[i].x)){
p0=p[i];
k=i;
}
}
swap(p[k],p[0]);
sort(p+1,p+n,cmp);
s[0]=p[0],s[1]=p[1];
top=1;
for(re int i=2;i<n;i++){
while(top&&compare(s[top-1],p[i],s[top])>=0)top--;
s[++top]=p[i];
}
}
inline ll dis(node a,node b){
return 1ll*(a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+1ll*(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y);
}
ll getmax(){
ll tmp=0;
if(top==1){
return dis(s[0],s[1]);
}
s[++top]=s[0];
int j=2;
for(re int i=0;i<top;i++){
while(compare(s[i],s[i+1],s[j])<compare(s[i],s[i+1],s[j+1])){
j=(j+1)%top;
}
tmp=max(tmp,max(dis(s[i],s[j]),dis(s[i+1],s[j])));
}
return tmp;
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(isdigit(ch)){x=x*10+(ch^48);ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int main(){
#ifdef LawrenceSivan
freopen("aa.in","r",stdin);
freopen("aa.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n=read();
for(re int i=0;i<n;i++){
p[i].x=read();p[i].y=read();
}
find();
ans=getmax();
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}
|
闵可夫斯基和:
定义:
闵可夫斯基和 $(Minkowski\ sum)$是两个欧几里得空间的点集的和,也称为这两个空间的膨胀集,以德国数学家闵可夫斯基命名。点集A与B的闵可夫斯基和被定义为:
$A+B={ a+b|a∈A,b∈B}$
若推广至流形的连续集,闵可夫斯基和从几何上的直观体现即是A集合沿B的边际连续运动一周扫过的区域与B集合本身的并集,也可以是B沿着A的边界连续运动扫过区域与A自身的并集。
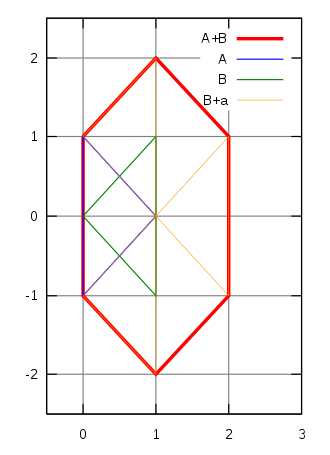
求法:
通过几何直观体现我们可以发现,其实闵可夫斯基和上的每一个边都是由原来的凸包平移得来的。于是我们的闵可夫斯基和其实就是要合并两个凸包。
针对其中任意一个凸包,首先极角已经是有序的了,于是在合并过程中,我们只需要进行归并排序,将两个凸包进行合并就可以了。
例题:P4557 [JSOI2018]战争
题意:给出两个点集A,B,以及q次询问。对于每次询问,给出一个向量,然后点集B向向量平移,若平移后的点集A与点集B构成的两个多边形存在交点则输出1,否则输出0。
通过读题我们可以知道,如果平移其中一个凸包后与另一个凸包有交点,那么一定满足:$a∈A,b∈B$,若移动向量为$c$,则存在$b+c=a$,移项得到$c=a-b$,,于是我们可以构造出一个闵可夫斯基和$C={ a+(-b)}$,之后我们只需要判断移动向量是否在我们构造的$C$中就可以了。
判断向量是否在凸包内:
判断方法:首先判断和边界的关系,之后找到与其极角相邻的两点,凭此判断即可。
需要注意的是,我们的原点$(0,0)$是A[1]
ll inside(node a){
if(a*A[1]>0||A[tot]*a>0) return 0;
ll pos=lower_bound(A+1,A+tot+1,a,cmp2)-A-1;
return (a-A[pos])*(A[pos%tot+1]-A[pos])<=0;
}
|
求凸包:
inline void convex(node *B,ll &n){
sort(B+1,B+1+n,cmp1);
p=B[1];
st[top=1]=1;
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
B[i]=B[i]-p;
}
sort(B+2,B+1+n,cmp2);
for(re ll i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(top>1&&(B[i]-B[st[top-1]])*(B[st[top]]-B[st[top-1]])>=0)top--;
st[++top]=i;
}
for(re ll i=1;i<=top;i++){
B[i]=B[st[i]]+p;
}
n=top,B[n+1]=B[1];
}
|
合并两个凸包:
inline void Minkowski(){
for(re ll i=1;i<n;i++){
s1[i]=C1[i+1]-C1[i];
s1[n]=C1[1]-C1[n];
}
for(re ll i=1;i<m;i++){
s2[i]=C2[i+1]-C2[i];
s2[m]=C2[1]-C2[m];
}
A[tot=1]=C1[1]+C2[1];
ll cnt1=1,cnt2=1;
while(cnt1<=n&&cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+(s1[cnt1]*s2[cnt2]>=0?s1[cnt1++]:s2[cnt2++]);
while(cnt1<=n)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s1[cnt1++];
while(cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s2[cnt2++];
}
|
CODE:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define re register
const int maxn=1e5+5;
const int maxm=1;
ll n,m,q;
ll st[maxn],top=1,tot;
struct node{
ll x,y;
node operator - (node A) {return (node){x-A.x,y-A.y};}
node operator + (node A) {return (node){x+A.x,y+A.y};}
ll operator * (node A) const {return x*A.y-y*A.x;}
ll len() const {return x*x+y*y;}
}s1[maxn],s2[maxn],A[maxn],C1[maxn],C2[maxn],p;
inline bool cmp1(node A,node B){
return A.y<B.y||(A.y==B.y&&A.x<B.x);
}
inline bool cmp2(node A,node B){
return A*B>0||(A*B==0&&A.len()<B.len());
}
inline void convex(node *B,ll &n){
sort(B+1,B+1+n,cmp1);
p=B[1];
st[top=1]=1;
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
B[i]=B[i]-p;
}
sort(B+2,B+1+n,cmp2);
for(re ll i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(top>1&&(B[i]-B[st[top-1]])*(B[st[top]]-B[st[top-1]])>=0)top--;
st[++top]=i;
}
for(re ll i=1;i<=top;i++){
B[i]=B[st[i]]+p;
}
n=top,B[n+1]=B[1];
}
inline void Minkowski(){
for(re ll i=1;i<n;i++){
s1[i]=C1[i+1]-C1[i];
s1[n]=C1[1]-C1[n];
}
for(re ll i=1;i<m;i++){
s2[i]=C2[i+1]-C2[i];
s2[m]=C2[1]-C2[m];
}
A[tot=1]=C1[1]+C2[1];
ll cnt1=1,cnt2=1;
while(cnt1<=n&&cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+(s1[cnt1]*s2[cnt2]>=0?s1[cnt1++]:s2[cnt2++]);
while(cnt1<=n)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s1[cnt1++];
while(cnt2<=m)++tot,A[tot]=A[tot-1]+s2[cnt2++];
}
ll inside(node a){
if(a*A[1]>0||A[tot]*a>0) return 0;
ll pos=lower_bound(A+1,A+tot+1,a,cmp2)-A-1;
return (a-A[pos])*(A[pos%tot+1]-A[pos])<=0;
}
inline ll read(){
ll x=0, f=1;char ch=getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while (isdigit(ch)){x=x*10+(ch^48);ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int main() {
#ifdef LawrenceSivan
freopen("aa.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("aa.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
n=read();m=read();q=read();
for(re ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
C1[i].x=read();C1[i].y=read();
}
convex(C1,n);
for(re ll i=1;i<=m;i++){
C2[i].x=-read();C2[i].y=-read();
}
convex(C2,m);
Minkowski();
convex(A,tot);
p=A[1];
for(re ll i=tot;i>=1;i--)A[i]=A[i]-A[1];
while(q--){
A[0].x=read();A[0].y=read();
printf("%lld\n",inside(A[0]-p));
}
return 0;
}
|